- Unified Compliance Knowledge Base
- Common Controls Hub FAQs
- Common Controls Hub Basics
-
Unified Compliance FAQs
-
Common Controls Hub FAQs
-
Compliance Dictionary FAQs
-
Research FAQs
-
Mapper FAQs
-
Partner FAQs
-
OEM FAQs
-
Common Controls Hub Deep Dive
-
Mapper Deep Dive
- Cataloging Authority Documents
- Cataloging Private Authority Documents
- Map a Citation
- Tag Citation
- Match Citation to a Control
- Match a Citation to a Control (Private Authority Documents)
- Add Audit Question
- Citation Hierarchy
- Citation Hierarchy (Private Authority Documents)
- Add Dictionary Terms
- Asset
- Configurable Item
- Configuration Setting
- Data Content
- Organization
- Organizational Task
- Record Category
- Record Example
- Role
- Triggering Event
- Nonstandard Term
-
Mapper Guides
-
API Developers
-
Contact Support
What is the difference between an Implied, Mandated, and an Implementation Control?
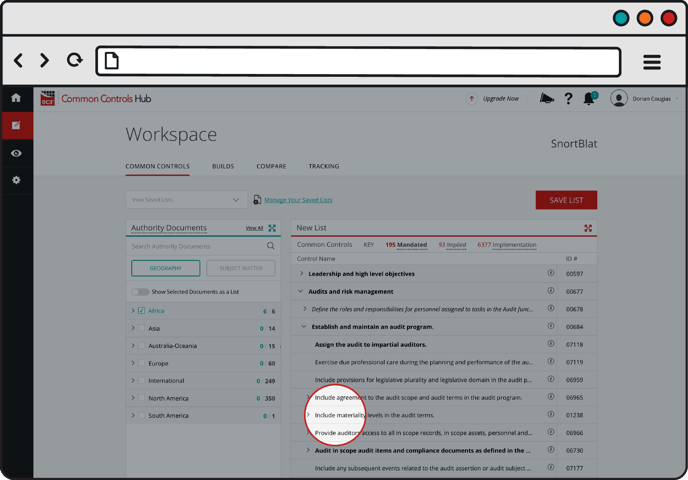
Mandated Control
A mandated Control is the Common Control linked to the Citation(s) from the Authority Document(s) selected by the organization. They are listed in Bold font.
Mandated Controls must be:
- Assigned to roles for accountability
- Tracked to completion
Example:

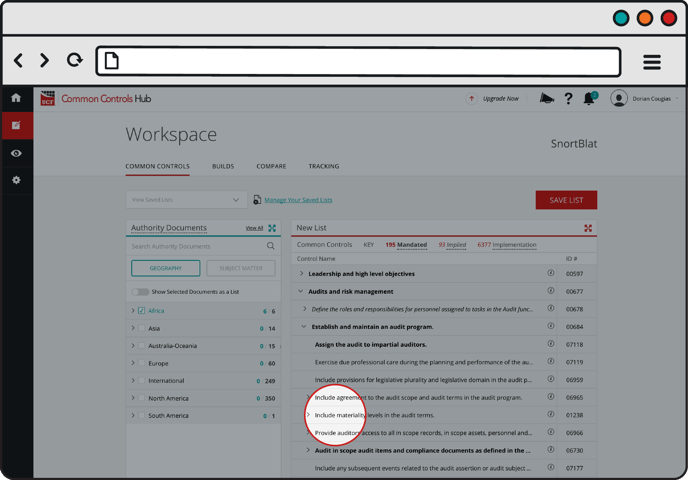
Implied Control
The Common Control(s) in the parentage of Mandated Controls, which are not otherwise mandated. They are listed in italic font.
Implied Controls:
- Are found within each Mandated Control's genealogy
- Are not mandated by any of the Authority Documents the organization has chosen to employ
- Do not have to be assigned for accountability
- Do not have to be tracked to completion
Example:

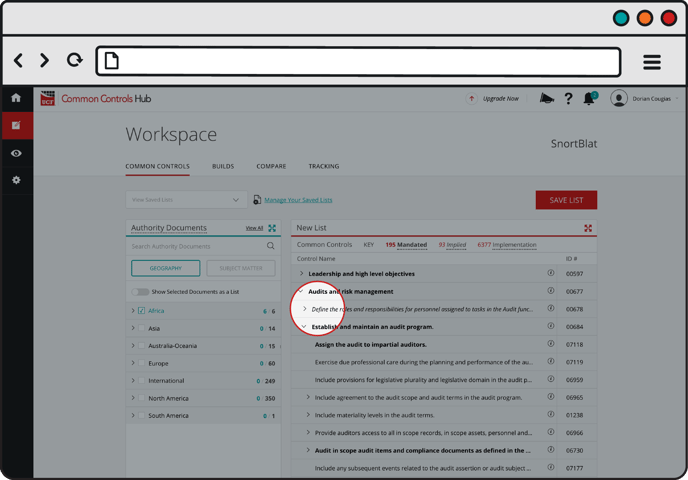
Implementation Controls
Non-Mandated Common Control(s) that are children of Mandated Controls. They are listed in plain text.
Implementation Controls:
- Provide details not found in Mandated Controls regarding how to carry out the Mandated Control.
- Are not mandated by any of the Authority Documents the organization has chosen to employ
- Do not have to be assigned for accountability
- Do not have to be tracked to completion
Example: